Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Kankyo To Kenko, 28(2), p.129 - 139, 2015/06
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Atsushi
Kankyo To Kenko, 12(2), p.198 - 207, 2008/06
Since mutation was induced in maize with X-rays by Stadler in 1928, a great deal of studies on the mutagenesis in plants by ionizing radiation have been carried out for both breeding and basic study. After 1960's, it have been found that ion beams show high relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of lethality, mutation, and so on, but the characteristics of ion beams on the mutation induction were not clearly elucidated yet. We have begun to investigate the characteristics of ion beams for inducing mutation from a molecular to a phenotypic level. Mutation induction rates were investigated using known visible  mutant phenotypes, such as
mutant phenotypes, such as 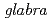 (
(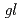 ) and transparent testa (
) and transparent testa ( ). These observations indicated that mutation frequencies induced by carbon ions were 20-fold higher than those induced by electrons. Molecular analyses showed that half of the mutants induced by ion beams possessed large DNA alterations, while the rest had point-like mutations. The common feature of mutations induced by ion beams is the deletion of several bases. It is possible that ion beams induce a limited number of large and irreparable DNA lesions, resulting in the production of null mutations that show a new mutant phenotype. Novel mutants, such as those that are UV-B resistant, have serrated petals and sepals, or lack anthocyanins, have been induced by 220 MeV carbon ions in
). These observations indicated that mutation frequencies induced by carbon ions were 20-fold higher than those induced by electrons. Molecular analyses showed that half of the mutants induced by ion beams possessed large DNA alterations, while the rest had point-like mutations. The common feature of mutations induced by ion beams is the deletion of several bases. It is possible that ion beams induce a limited number of large and irreparable DNA lesions, resulting in the production of null mutations that show a new mutant phenotype. Novel mutants, such as those that are UV-B resistant, have serrated petals and sepals, or lack anthocyanins, have been induced by 220 MeV carbon ions in  . The mutated genes were found to encode novel and key proteins for each process. In chrysanthemum and carnation, several kinds of flower-color and flower-form mutants that have never been produced by
. The mutated genes were found to encode novel and key proteins for each process. In chrysanthemum and carnation, several kinds of flower-color and flower-form mutants that have never been produced by  -rays or X-rays were induced by carbon ions. These observations indicate that the characteristics of mutations induced by ion beams are high frequency and broad spectrum, and produce novel mutants. Many breeding programmes are using mutants induced by ion beams and successfully producing useful new crop varieties.
-rays or X-rays were induced by carbon ions. These observations indicate that the characteristics of mutations induced by ion beams are high frequency and broad spectrum, and produce novel mutants. Many breeding programmes are using mutants induced by ion beams and successfully producing useful new crop varieties.